Switch Mode  Power Supply
Power Supply
Switched-mode power supply
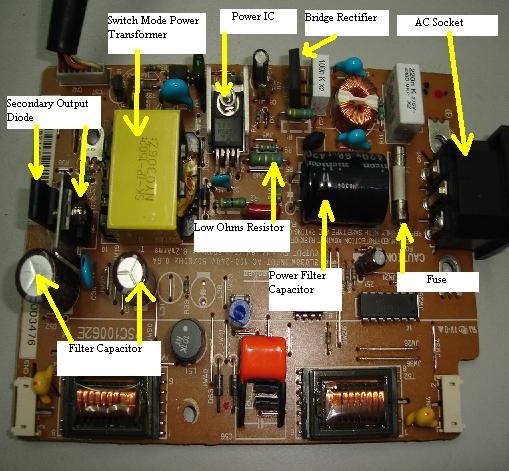

A switched-mode power supply (also switching-mode power supply and SMPS) is an electronic power supply unit (PSU) that incorporates a switching regulator. While a linear regulator maintains the desired output voltage by dissipating excess power in a pass power transistor, the SMPS rapidly switches a power transistor between saturation (full on) and cutoff (completely off) with a variable duty cycle whose average is the desired output voltage. The resulting rectangular waveform is low-pass filtered with an inductor and capacitor. The main advantage of this method is greater efficiency because the switching transistor dissipates little power in the saturated state and the off state compared to the semiconducting state (active region). Other advantages include smaller size and lighter weight (from the elimination of low frequency transformers which have a high weight) and lower heat generation due to higher efficiency. Disadvantages include greater complexity, the generation of high amplitude, high frequency energy that the low-pass filter must block to avoid electromagnetic interference (EMI), and a ripple voltage at the switching frequency and the harmonic frequencies thereof.
SMPS can be classified into four types according to the input and output waveforms:
- AC in, DC out: rectifier, off-line converter input stage
- DC in, DC out: voltage converter, or current converter, or DC to DC converter
- AC in, AC out: frequency changer, cycloconverter
- DC in, AC out: inverter
ATX Power Supply
The ATX (for Advanced Technology Extended) form factor was created by Intel in 1995. It was the first big change in computer case and motherboard design in many years. ATX overtook AT completely as the default form factor for new systems. ATX addressed many of the AT form factor's annoyances that had frustrated system builders. Other standards for smaller boards (including microATX, FlexATX and mini-ITX) usually keep the basic rear layout but reduce the size of the board and the number of expansion slot positions. In 2003, Intel announced the BTX standard, intended as a replacement for ATX. As of 2007[update] the ATX form factor remains the industry standard for do-it-yourselfers; BTX has however made inroads into pre-made systems, being adopted by computer makers like Dell, Gateway, and HP.
The official specifications were released by Intel in 1995, and have been revised numerous times since, the most recent being version 2.2,[1] released in 2004.
A full size ATX board is 305 mm wide by 244 mm deep (12" x 9.6" ). This allows many ATX form factor chassis to accept microATX boards as well.
AT Power Supply
In the area of IBM compatible personal computers, the AT form factor referred to the dimensions and layout (form factor) of the motherboard for the IBM AT. Like the IBM PC and IBM XT models before it, many third-party manufcturers produced motherboards compatible with the IBM AT form factor, allowing end users to upgrade their computers for faster processors. The IBM AT became a widely copied design during the booming home computer market in the 1980s. IBM clones made at the time began using AT compatible designs, contributing to its popularity. In the 1990s many computers still used AT and its variants. Since 1997, the AT form factor has been largely supplanted by ATX.
BTX Power Supply
BTX (for Balanced Technology Extended) is a form factor for PC motherboards, originally slated to be the replacement for the aging ATX motherboard form factor in late 2004 and early 2005. It has been designed to alleviate some of the issues that arose from using newer technologies (which often demand more power and create more heat) on motherboards compliant with the circa-1996 ATX specification. The ATX and BTX standards were both proposed by Intel. Intel's decision to refocus on low-power CPUs, after suffering scaling and thermal issues with the Pentium 4, has added some doubt to the future of the form factor. The first company to implement BTX was Gateway Inc, followed by Dell. Apple's Mac Pro utilizes the elements of the BTX design system as well but is not BTX compliant. However, future development of BTX retail products by Intel was canceled in September 2006
And Many Falowing Types Of SMPS
| Name | PCB Size (mm) |
|---|---|
| WTX | 356×425 |
| AT | 350×305 |
| Baby-AT | 330×216 |
| BTX | 325×266 |
| ATX | 305×244 |
| LPX | 330×229 |
| NLX | 254×228 |
| microATX | 244×244 |
| DTX | 244×203 |
| FlexATX | 229×191 |
| Mini-DTX | 203×170 |
| EBX | 203×146 |
| microATX (Min.) | 171×171 |
| Mini-ITX | 170×170 |
| EPIC (Express) | 165×115 |
| Nano-ITX | 120×120 |
| COM Express | 125×95 |
| ETX / XTX | 114×95 |
| Pico-ITX | 100×72 |
| PC/104 (-Plus) | 96×90 |
| mobile-ITX | 75×45 |